Describe the Role of Rna Polymerase in Transcription
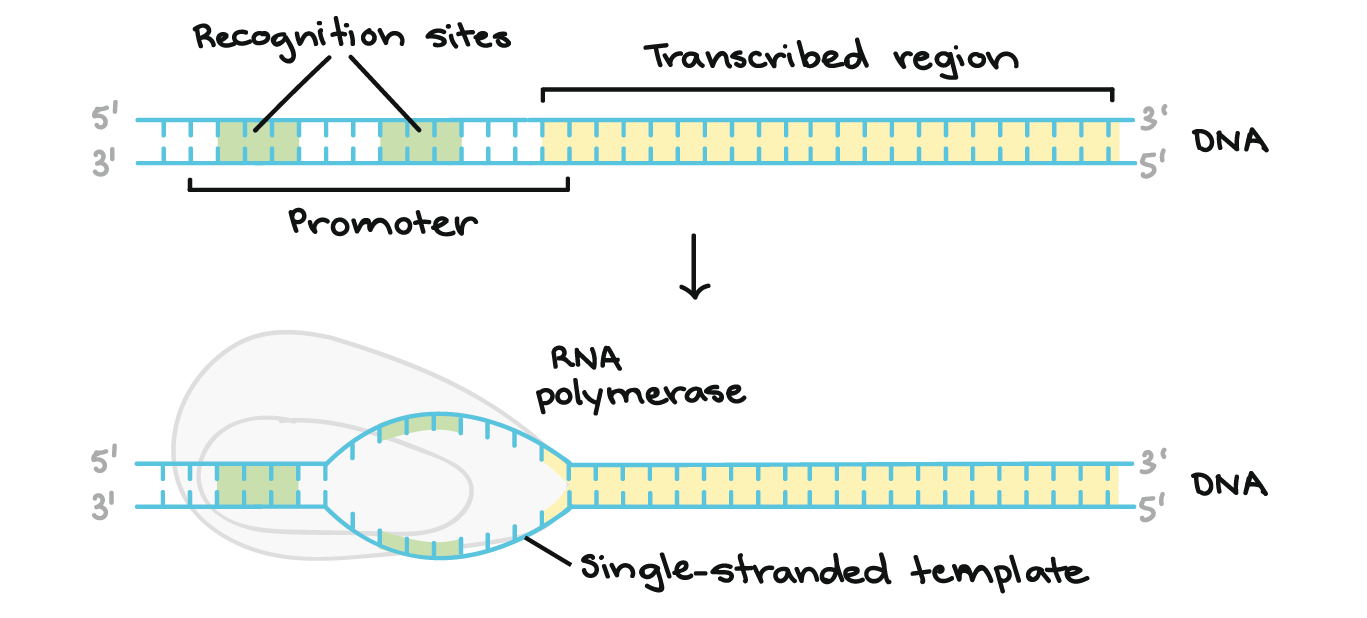
The rRNA molecules are considered structural RNAs because they have a cellular role but are not translated into protein. Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene directly or through helper proteins.
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
The effect of amanitin on the maximum elongation rate for the wild-type and modified RNA polymerases.
. This causes the double helix shape of the DNA to unwind. Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 MED1 a transcriptional coactivator plays an important role in the interaction. The RNA polymerase after initiation of RNA transcription loses the σ-factor but continues the process of RNA formation.
The need for this control group in the second experiment. Key Concept 3 Describe the role of RNA polymerase in the transcription process. Transcription by the RNA polymerase II Pol II enzyme occurs not only at annotated protein-coding genes but throughout the genome and is fundamentally important for most physiological processes.
The rRNA molecules are considered structural RNAs because they have a cellular role but are not translated into protein. The sequence of the RNA polymer is complementary to that of the template DNA and is synthesized in a 5 3 orientation. A Initiations sigma factor recognises the start signal and promotor region on DNA and the s sigma with RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and initiate transcription.
Transcription is the first process in regulating gene expression and RNA synthesis helps in the copying of genetic data from DNA to RNA. RNA polymerase is the main transcription enzyme. Role of Polymerase in Transcription in Bacteria.
Key Concept 3 Categories Questions. The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. Describe the role of RNA polymerase in the transcription process.
A nitrogenous base A pentose ribose sugar A phosphate group In a RNA monom. 100 14 ratings Answer The three structural components of an RNA nucleotide monomer are. RNA polymerase is the key enzyme in transcription it copys the DNA sequence in to RNA transcription which is later tr.
An official website of the United States government. Unlike bacterial cells where a single RNAP facilitates transcription there are. Heres how you know.
View the full answer Transcribed image text. Once the RNA polymerase reaches the termination region of. RNA polymerase I is located in the nucleolus a specialized nuclear substructure in which ribosomal RNA rRNA is transcribed processed and assembled into ribosomes Table 1.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply. New questions in Biology. What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes.
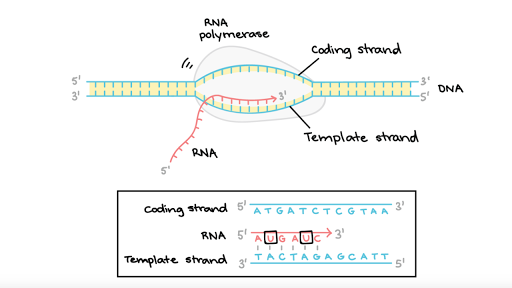
The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand. It protects the plant from. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Students will be able to. During transcription RNA Polymerase binds with upstream of the gene that is to be transcribed into mRNA. RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands the template strand as a template to make a new complementary RNA molecule.
An acceptable explanation of the role of RNA polymerase. Up to 24 cash back the role of RNA. RNA polymerase I is located in the nucleolus a specialized nuclear substructure in which ribosomal RNA rRNA is transcribed processed and assembled into ribosomes Table 1.
The role of RNA polymerase during transcription is that it examines the process of transcription data drawn into the new molecule of messenger RNA. B ElongationThe RNA polymerase after initiation of RNA transcription loses the s-factor but continues the process of. RNA polymerase RNAP is the enzyme responsible for transcription in eukaryotic cells.
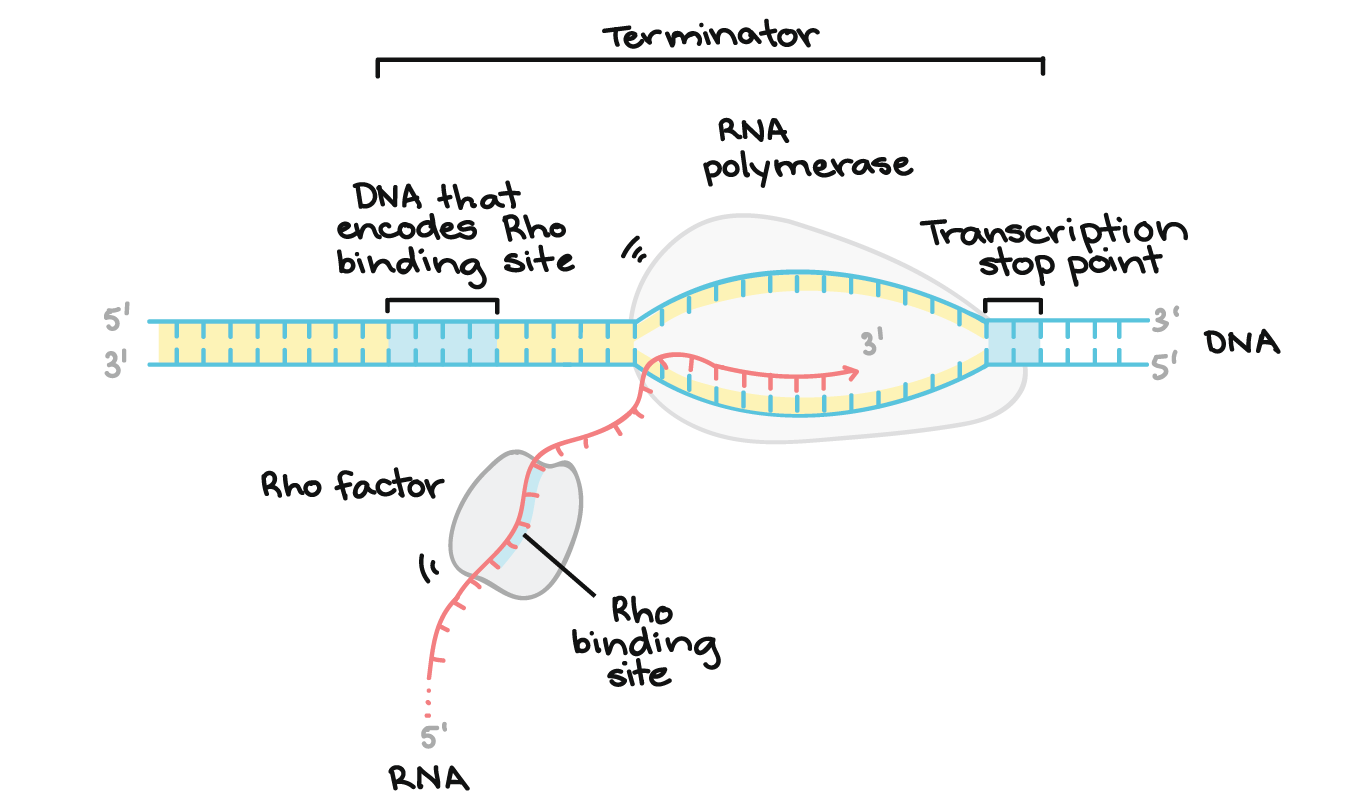
The RNA chain continues to grow until the RNA polymerase encounters a termination signal. View the full answer. - RNA polymerase joinsbonds the newly paired RNA nucleotide and the growing RNA strand with a covalent bond.
Explain sexual reproduction in fungi Choose all the statements which correctly describe the function of the outer covering in plants. Acceptable explanations include the following. σ sigma factor recognises the start signal and promotor region on DNA and the σ sigma with RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and initiates transcription.
It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. A control group missing from the second experiment. RNA Polymerase catalyzes a reaction that cleaves off two phosphates from an NTP and forms a phosphodiester linkage between the 3 end of the growing mRNA chain and the resulting ribonucleoside monophosphate during Transcription.
This review aims to describe the roles of SEs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases through multiple interactions of these factors as well as a future outlook on this issue. The dependent variable in the experiments. Outline the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA describe the process of transcription including the role of RNA polymerase s in prokaryotes and eukaryotes use knowledge of bases and base pairings to convert DNA sequences into mRNA sequences recall where transcription occurs in a eukaryotic cell describe post-transcriptional.
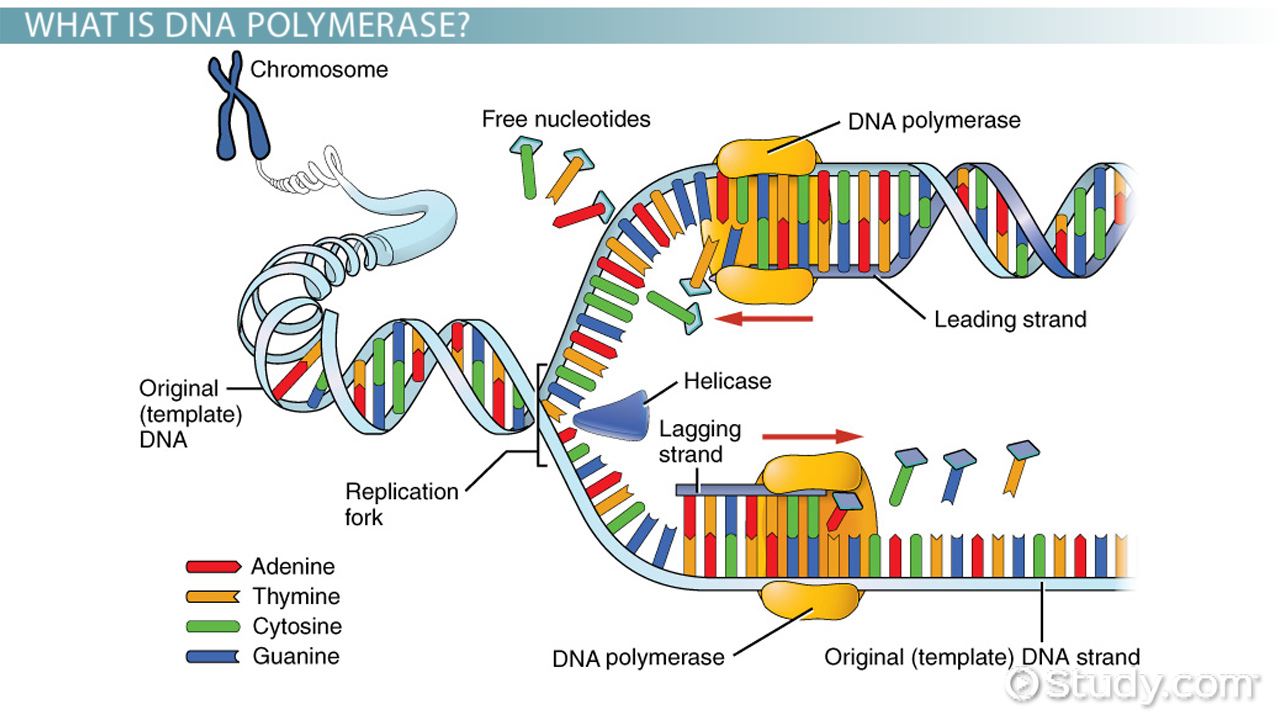
ATranscribes only snRNAs bTranscribes rRNAs 28S 18S and 585S. - RNA polymerase synthesizes a new RNA molecule based on a DNA template by matching the current DNA base with the proper RNA complement. As it moves the polymerase unwinds the template DNA over about 17 base pairs less than two turns of the double helix in the region of transcription.
Describe the process of transcription including the role of RNA polymerase s in prokaryotes and eukaryotes use knowledge of bases and base pairings to convert DNA sequences into mRNA sequences recall where transcription occurs in a eukaryotic cell. A RNA polymerase RNAP or ribonucleic acid polymerase is a multi subunit enzyme that catalyzes the process of transcription where an RNA polymer is synthesized from a DNA template. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
After RNA polymerase has passed the DNA strands reform the duplex. This process builds the RNA complimentary to the DNA template.
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

Noncoding Rnas Set The Stage For Rna Polymerase Ii Transcription Trends In Genetics

Question Video Recalling The Role Of Rna Polymerase In Transcription Nagwa

Rna Polymerase Ii An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
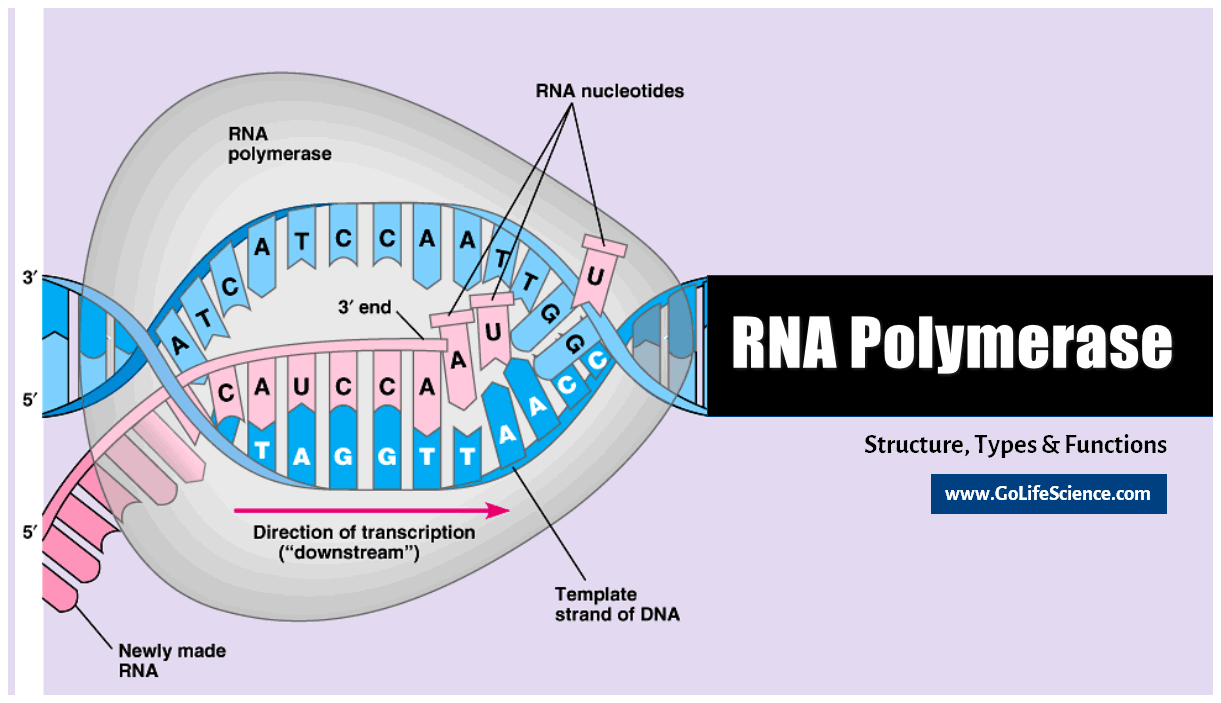
Rna Polymerase The Rna Synthesis Enzyme Structure And Its Types

State Diagrams Of Rna Polymerase A The Model Of The Main Download Scientific Diagram
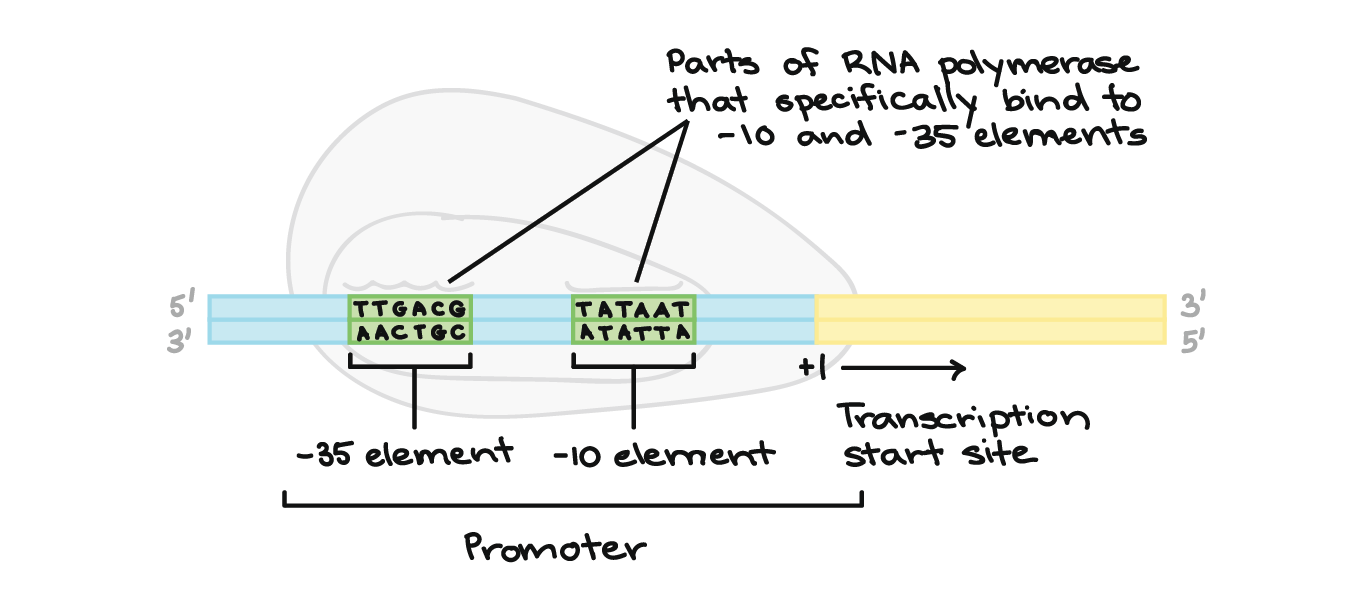
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
How Would Rna Polymerase Be Affected If The Repressor Protein Were Not Bound To The Proper Site On A Gene Socratic

Rna Transcription Microbiology
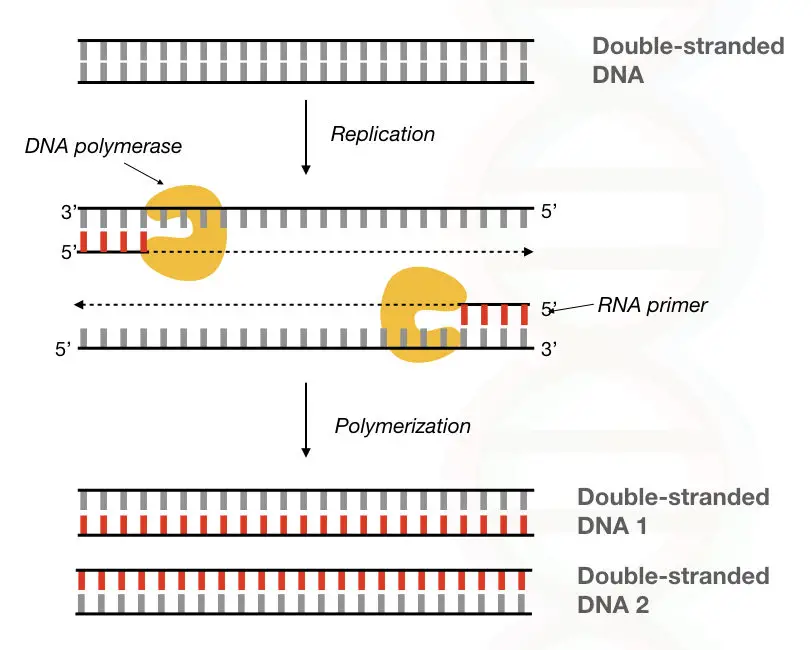
Comparison Between Dna Polymerase Vs Rna Polymerase
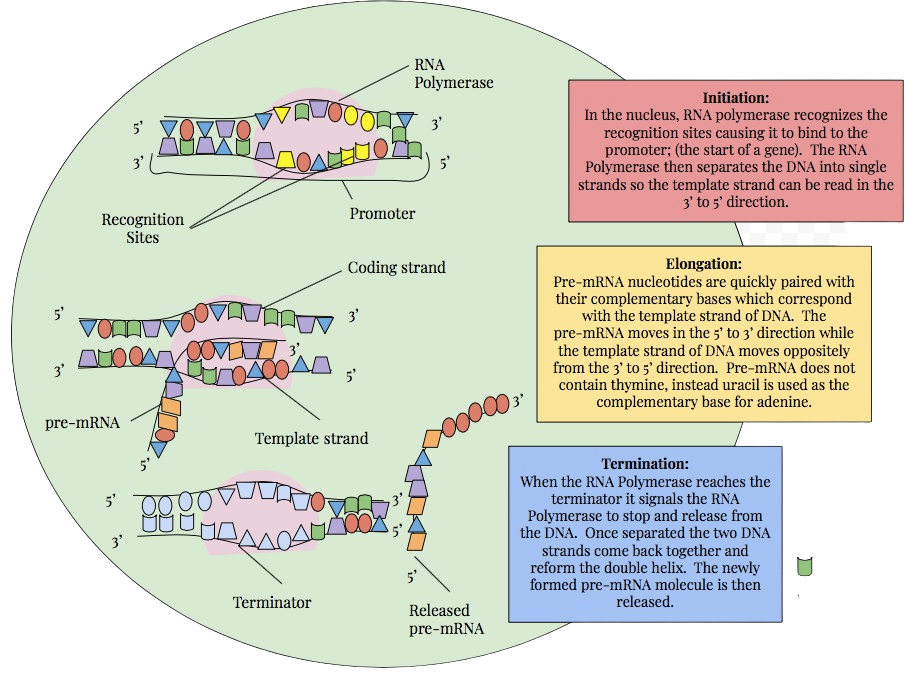
Rna Transcription Study Guide Inspirit

Rna Polymerase Overview Role In Transcription Expii

Rna Polymerase Function And Definition Technology Networks

Rna Polymerase Function And Definition Technology Networks

Rna Transcription An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Termination Of Transcription By Rna Polymerase Ii Boom Trends In Genetics

Comments
Post a Comment